Here you will learn about scale factor, including enlarging a shape by a scale factor on a grid. You will extend this to learn about fractional scale factors and how to calculate scale factors.
Students will first learn about scale factor as part of geometry in 7 th grade and continue to work with scale factor in high school.
A scale factor is a ratio between two corresponding sides of similar shapes. A scale factor describes how much a shape has been scaled up or down.
To scale a shape up or down, you multiply every side length of a shape by the scale factor to increase or decrease the size. The sizes of the angles do not change. Changing a shape by a scale factor greater than \bf will make the shape a larger figure. Scaled shapes can be referred to as images, while original shapes are referred to as preimages.
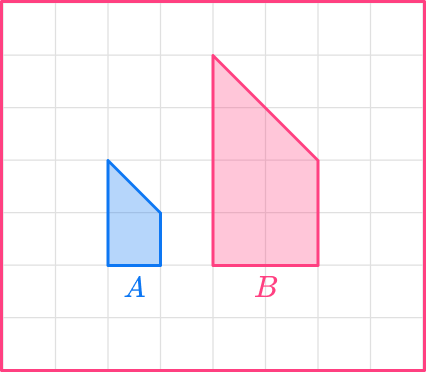
For example, shape A that has been enlarged by scale factor 2 to give shape B.

The corresponding angles are identical but each side in shape B is double the size of the original figure.
The two shapes are similar figures. Enlarging a shape by a scale factor between \bf and \bf will make the shape smaller. This is often written as a fraction or a decimal and is known as a fractional scale factor.
Here, shape A has been enlarged by scale factor \cfrac to get shape B.
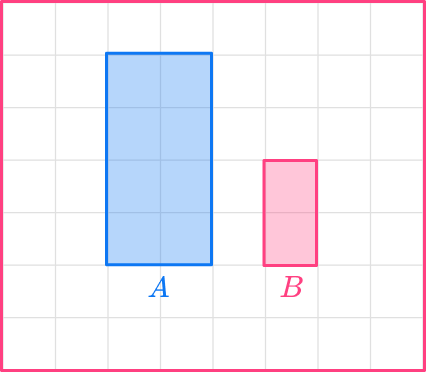
If you look at the corresponding sides in the scale drawing, each side in shape B is half the size of the original shape. The corresponding angles are identical. The two shapes are similar figures.